基本理论
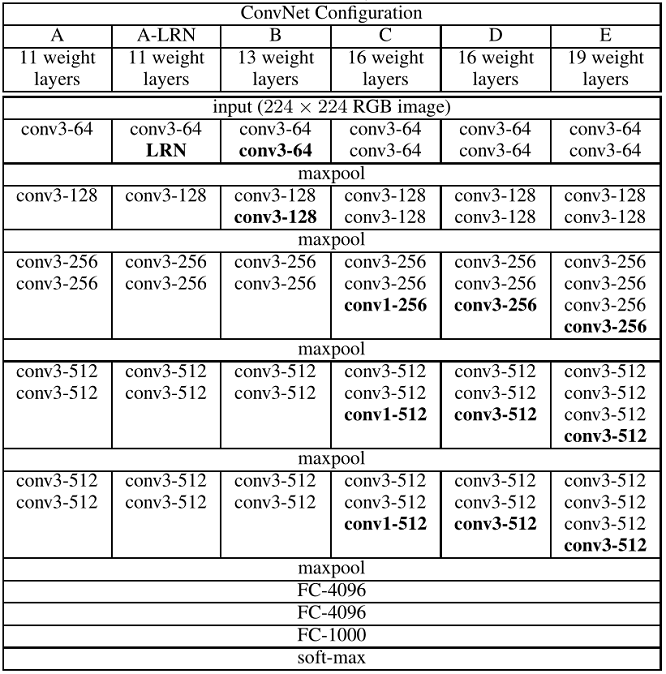
图 1.1
如图 1.1 所示,VGG 是一个网络系列,从 VGG-11(8 层卷积层,3 层全连接层)到 VGG-19(16 层卷积层,3 层全连接层)。输入图像的大小都是 $224\times224$,然后对图像进行均值化处理;卷积过程都是采用固定大小的卷积核,即 $3\times3$,步长 $s=1$,$Same$ 方式,填充 $p=1$,卷积后大小不变,仅仅深度改变,由图 1.1 可以看出,$C$ 网络结构采用了 $1\times1$ 的卷积核,主要作用:$1\times1$ 的卷积核主要是针对 channel 维度的,可以实现对 channel 降维或者升维,例如 $6 \times 6 \times 32$ 的feature map 在 16 个 $1 \times 1 $ 的卷积核上做卷积,结果为 $6 \times 6 \times 16$,其实也可以换个角度看,如图 1.2 所示,从输入的 feature map 中取一块 $1 \times 1$ 的区域,深度为 32,然后与 16 个 $1 \times 1 $ 的卷积核进行卷积,也就是一个很小的全连接神经网络,输入是 32 个数字,输出是 16 个数字,然后在 $6 \times 6$ 的区域重复此过程,所以有时候也称为 Network in Network;可以保持 feature map 大小不变的情况下,增加非线性(主要是通过卷积层后面的激活函数实现的)。池化层采用 $2 \times 2$ 固定大小的池化窗口,步长 $s=2$。三层全连接层,前两层全连接层 channels 大小为 4096,最后一层输出层 channels 大小为 1000。另外所有隐藏层全部采用 ReLU 激活函数。前两层的全连接层训练时进行 Dropout。
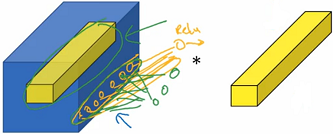
图 1.2
网络结构分析
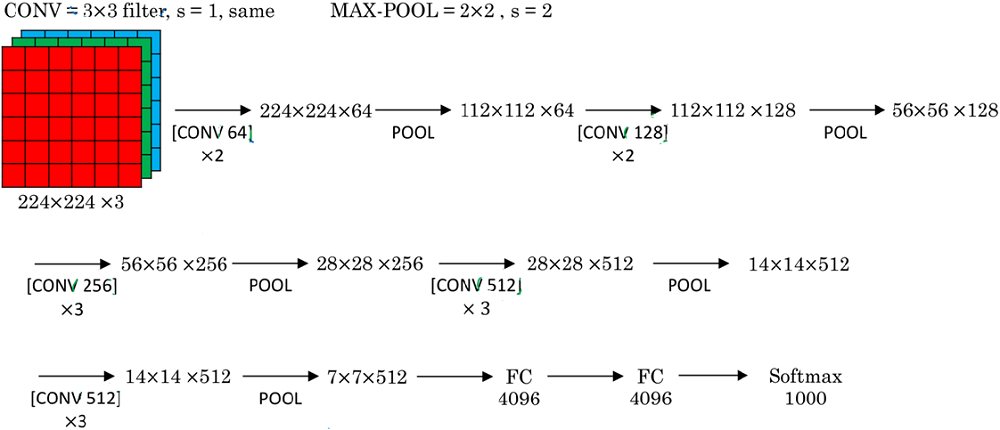
图 2.1
1-2层 卷积层
conv:输入的 $shape$ 为 $224\times224\times3$,$64$ 个 $3\times3$ 的卷积核,步长为 $s=1$,$Same$ 方式。输出的 $shape$ 为 $224\times224\times64$。max-pool:输入的 $shape$ 为 $224\times224\times64$,池化参数 $f=2,s=2$,输出的 $shape$ 为 $112\times112\times64$。
3-4层 卷积层
conv:输入的 $shape$ 为 $112\times112\times64$,$128$ 个 $3\times3$ 的卷积核,步长为 $s=1$,$Same$ 方式。输出的 $shape$ 为 $112\times112\times128$。max-pool:输入的 $shape$ 为 $112\times112\times128$,池化参数 $f=2,s=2$,输出的 $shape$ 为 $56\times56\times128$。
5-7层 卷积层
conv:输入的 $shape$ 为 $56\times56\times128$,$256$ 个 $3\times3$ 的卷积核,步长为 $s=1$,$Same$ 方式。输出的 $shape$ 为 $56\times56\times256$。max-pool:输入的 $shape$ 为 $56\times56\times256$,池化参数 $f=2,s=2$,输出的 $shape$ 为 $28\times28\times256$。
8-10层 卷积层
conv:输入的 $shape$ 为 $28\times28\times256$,$512$ 个 $3\times3$ 的卷积核,步长为 $s=1$,$Same$ 方式。输出的 $shape$ 为 $28\times28\times512$。max-pool:输入的 $shape$ 为 $28\times28\times512$,池化参数 $f=2,s=2$,输出的 $shape$ 为 $14\times14\times512$。
11-13层 卷积层
conv:输入的 $shape$ 为 $14\times14\times512$,$512$ 个 $3\times3$ 的卷积核,步长为 $s=1$,$Same$ 方式。输出的 $shape$ 为 $14\times14\times512$。max-pool:输入的 $shape$ 为 $14\times14\times512$,池化参数 $f=2,s=2$,输出的 $shape$ 为 $7\times7\times512$。
14层 全连接层
fc:$7\times7\times512\rightarrow4096$。Dropout:0.5。
15层 全连接层
fc:$4096\rightarrow4096$。Dropout:0.5。
16层 全连接层
fc:$4096\rightarrow1000$。
代码分析
相关代码放在 github 上,大家可以移步 github 下载,分以下几部分:
generate_vgg16.py:训练数据;vgg16.py:VGG16 模型;train_vgg16.py:训练 VGG16 模型;predict_vgg16.py:验证 VGG16 模型。
训练数据
采用 Kaggle Dogs vs. Cats Redux Competition 作为训练数据,在已经训练好的 VGG16 模型上进行迁移学习,只训练后面三层的全连接层,对猫、狗进行分类。我把训练数据上传到腾讯云cos上,可以下载 train.zip,根据图片的文件名,可以对狗、猫的图片进行标注 cat:0, dog:1,数据分为训练集和验证集(85/15),并分别保存在 train.txt 和 val.txt,格式为 filename label。
面开始我们的数据处理吧。
mkdir data
cd data
wget http://tensorflow-1253902462.cosgz.myqcloud.com/alexnet/train.zip
unzip -q train.zip
cd ..
python
from generate_vgg16 import ImageDataGenerator
ImageDataGenerator.get_image_path_label()
按照上面一步一步执行完,会生成 train.txt 和 val.txt,文件内容如下面所示:
data/train/dog.7412.jpg 1
data/train/cat.1290.jpg 0
训练 VGG16 模型
模型结构具体细节可以参考第二部分的 模型分析 。我们在已经训练好的 VGG16 上进行迁移学习,具体做法:前十三层卷积层的权重和偏置不进行训练,直接赋值已经训练好的参数 vgg16_weights.npz,后面三层全连接随机初始化,然后进行训练。原始的 VGG16 是针对 $1000$ 个分类,最后一层的 $softmax$ 输出 $1000$ 个类别,我们这里仅仅对猫、狗进行分类,所以 $softmax$ 输出 $2$ 个类别。同样我把 vgg16_weights.npz 上传到腾讯云 cos 上,方便大家下载。
下面开始我们的模型训练吧。
wget http://tensorflow-1253902462.cosgz.myqcloud.com/vgg16/vgg16_weights.npz
nohup python train_vgg16.py &
tail -f train_vgg16.log
大概训练一个多小时,在验证集上准确率达到 98.5%,所以把训练过程写到 train_vgg16.log 文件中,nohup 可以防止进程被 SIGHUP 信号干掉。另外每训练完一个 epoch,会保存一次训练结果,如果中途中断训练,重新开始训练先读取上次训练结果,可以有效地防止从头开始训练。打开你的机器 9090 端口,可以通过 $tensorboard$ 查看训练的动态过程,如图 3.1和图 3.2 所示,分别是训练集上的准确度和损失函数。
tensorboard --port 9090 --logdir=/home/ubuntu/machinelearning/vgg16/train_vgg16
http://IP:9090/
下面可以喝杯茶耐心地等待训练过程啦,当然如果你不想等待训练过程,我这里也提供已经训练好的模型,放在腾讯云 cos 上,大家可以下载 VGG16_Dogs_Cats_model。
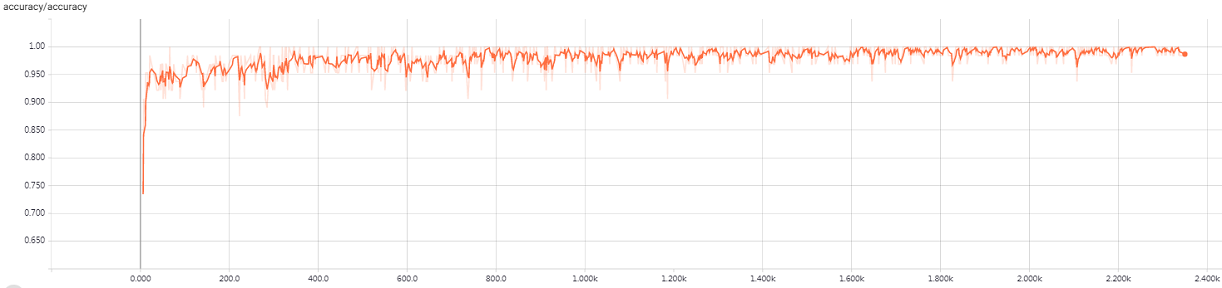
图 3.1
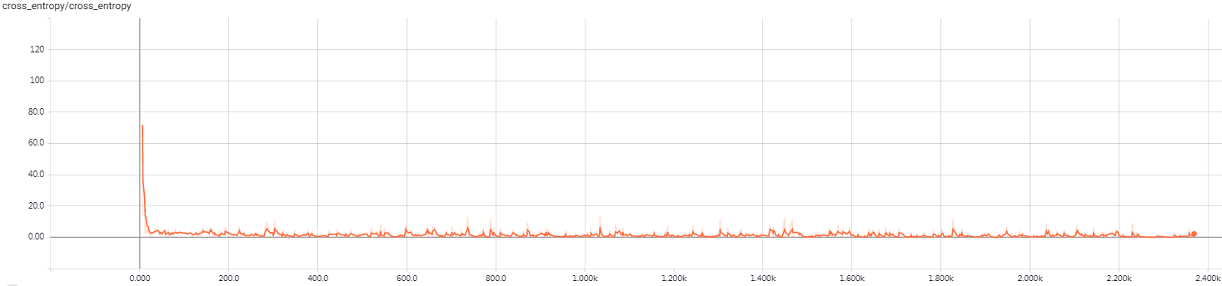
图 3.2
验证 AlexNet 模型
主要实现两个功能:
ImageNet 图像分类
直接读取 vgg16_weights.npz 的权重,我自己随便在 Google 上下载三张图片放在腾讯云 cos 上,大家可以下载或者自己去百度下载图片。 下面开始我们的图片分类,取概率最大的top5
wget http://tensorflow-1253902462.cosgz.myqcloud.com/alexnet/Elephant.jpg
wget http://tensorflow-1253902462.cosgz.myqcloud.com/alexnet/cat.jpg
wget http://tensorflow-1253902462.cosgz.myqcloud.com/alexnet/dog.jpg
python predict_vgg16.py 1 Elephant.jpg
输出:
tusker 0.647837
African elephant, Loxodonta africana 0.310758
Indian elephant, Elephas maximus 0.0413153
water buffalo, water ox, Asiatic buffalo, Bubalus bubalis 1.25728e-05
Arabian camel, dromedary, Camelus dromedarius 1.18659e-05
当然你也可以试试对 cat.jpg、dog.jpg 分类,看看结果。
Cats vs. Dogs 分类
仅仅对猫、狗分类,所以我们只能使用 cat.jpg、dog.jpg 图片。
python predict_vgg16.py 2 cat.jpg
输出:
cat
python predict_vgg16.py 2 dog.jpg
输出:
dog
参考
Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition
